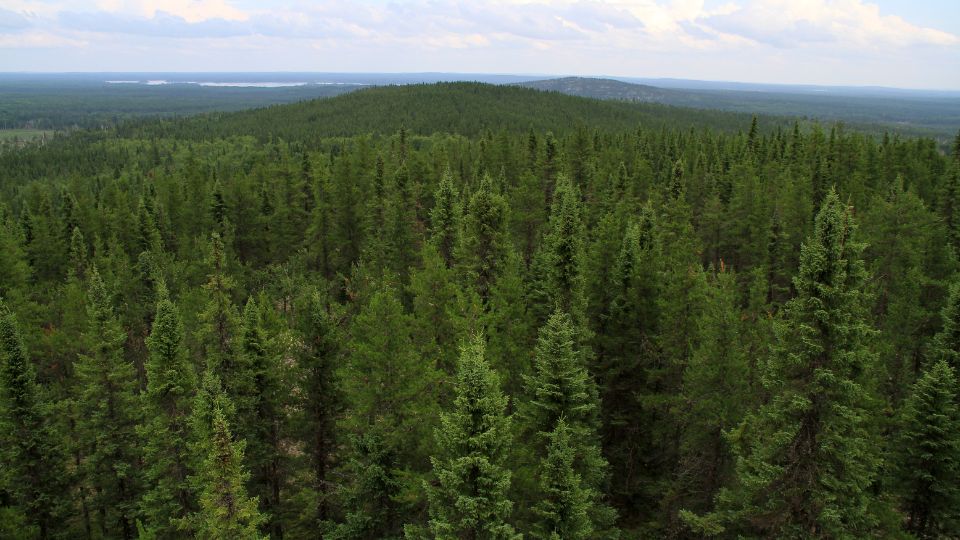
Boreal Forest Biome

A biome is a large, distinct biological community characterized by specific types of plants and animals that are adapted to a particular set of environmental conditions. The boreal forest biome is one of the largest biomes on Earth, spanning across North America, Europe, and Asia. It is also known as the taiga or coniferous forest biome.
What is Boreal Forest Biome?
The boreal forest biome is characterized by its coniferous trees, such as spruce, pine, and fir, which are adapted to the cold temperatures and short growing seasons of the region. The canopy of these trees is often so dense that little light reaches the forest floor, resulting in a relatively low diversity of understory vegetation. The soil is typically nutrient-poor and acidic, with a high content of organic matter.
The boreal forest biome has a distinct seasonal cycle, with long, cold winters and short, mild summers. The growing season is typically only a few months long, and during this time, there is a burst of activity as plants and animals take advantage of the warmer temperatures and increased sunlight. The short growing season can limit the diversity of plant life within the forest.
The boreal forest biome is home to a wide variety of wildlife, including mammals, birds, fish, and reptiles. Some common mammals include moose, black bear, gray wolf, and lynx, while birds like the Spruce Grouse, Wood Duck, and Ruffed Grouse are also found in these habitats. Boreal forests also host a wide variety of fish species in its rivers and streams, including brook trout, lake trout, and arctic grayling.
The boreal forest biome plays an important role in the global carbon cycle, as these forests store large amounts of carbon and are critical for regulating the global climate. They also provide habitat for a wide variety of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else on Earth. However, these forests are under threat from human activities such as logging, mining, and oil and gas development, making conservation efforts crucial to preserve these vital ecosystems for the future.
Boreal Forest Biome Plants List
The boreal forest biome is characterized by its coniferous trees, such as spruce, pine, and fir. The list of the most common plants found in the boreal forest biome includes:
- Black spruce (Picea mariana)
- Jack pine (Pinus banksiana)
- White spruce (Picea glauca)
- Balsam fir (Abies balsamea)
- Larch (Larix spp.)
- Eastern hemlock (Tsuga canadensis)
- Paper birch (Betula papyrifera)
- Quaking aspen (Populus tremuloides)
- Tamarack (Larix laricina)
- White pine (Pinus strobus)
The understory of boreal forest is relatively low in diversity and is usually dominated by ground-hugging plants such as mosses, lichens, and ferns. Some of the common understory plants are:
- Labrador tea (Rhododendron groenlandicum)
- Blueberry bushes (Vaccinium spp.)
- Cranberry (Vaccinium oxycoccus)
- Bog rosemary (Andromeda polifolia)
- Cloudberry (Rubus chamaemorus)
- Bearberry (Arctostaphylos uva-ursi)
- Cowberry (Vaccinium vitis-idaea)
- Crowberry (Empetrum nigrum)
- Lingonberry (Vaccinium vitis-idaea)
- Wild cranberry (Vaccinium oxycoccos)
In conclusion, the boreal forest biome is a large and distinct ecosystem found in the cold, northern regions of the world. It is characterized by its coniferous trees, such as spruce, pine, and fir, as well as a distinct seasonal cycle of long, cold winters and short, mild summers. The boreal forest biome is home to a wide variety of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else on Earth.
These forests play an important role in the global carbon cycle, as they store large amounts of carbon and are critical for regulating the global climate. However, boreal forests are under threat from human activities such as logging, mining, and oil and gas development, making conservation efforts crucial to preserve these vital ecosystems for the future. It is important to protect these unique and fragile ecosystems to maintain their ecological integrity and biodiversity for future generations.