Grassland Habitat
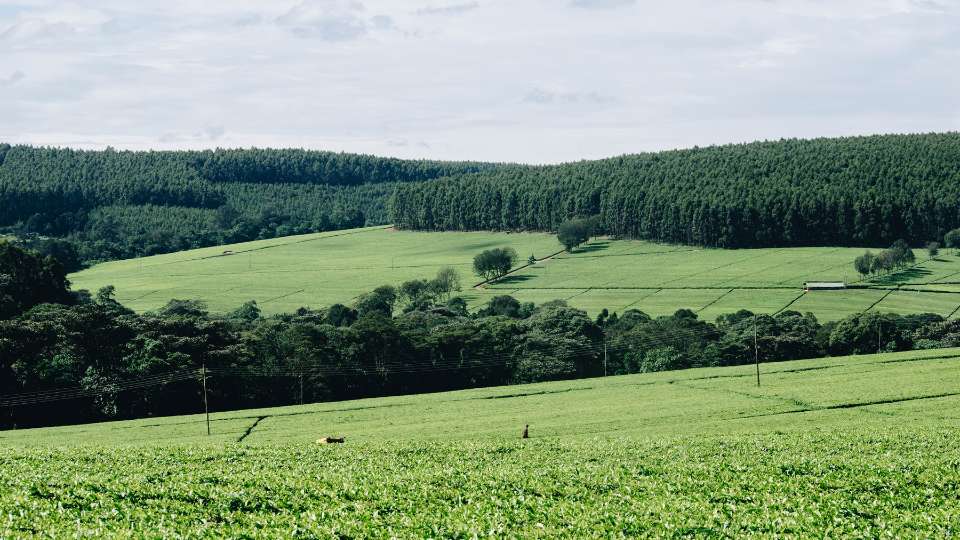

Grasslands, also known as prairies or savannas, are a common habitat for plants that are characterized by the presence of grasses, herbs, and other types of non-woody plants. They are found in many different regions, including the Great Plains of North America, the steppes of Asia, and the savannas of Africa. In this article, we will take a closer look at the characteristics of grasslands as a habitat for plants, the different types of grasslands and their ecological importance.
Characteristics of Grassland Habitats
Grasslands are characterized by the presence of grasses, herbs, and other types of non-woody plants, as well as by a distinctive layer of soil called the sod, which is composed of the roots, rhizomes and stolons of grasses. These plants are adapted to the specific conditions of the environment, such as the amount of sunlight, soil type, and moisture levels.
Grassland habitats are also characterized by their seasonal patterns of growth and reproduction. For example, many grassland plants have evolved to take advantage of the rainy season by germinating and growing quickly, then going dormant or dying back during the dry season. This allows them to survive in areas where water is scarce and temperatures can fluctuate widely.
Grassland habitats can vary in terms of vegetation density. In some grasslands, the grasses and other plants are so dense that it can be difficult for animals to move through the area, while in other grasslands, the vegetation is more scattered and less dense. The density of vegetation in a grassland habitat can be influenced by factors such as precipitation levels, temperature, and soil quality.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Grasses and Herbs | Grasslands are characterized by the presence of grasses, herbs, and other types of non-woody plants. These plants are adapted to the specific conditions of the environment, such as the amount of sunlight, soil type, and moisture levels. |
| Sod | A distinctive layer of soil called the sod, which is composed of the roots, rhizomes, and stolons of grasses. |
| Seasonal Patterns | Grassland habitats are also characterized by their seasonal patterns of growth and reproduction, many grassland plants have evolved to take advantage of the rainy season by germinating and growing quickly, then going dormant or dying back during the dry season. |
| Vegetation density | The density of vegetation in a grassland habitat can vary and can be influenced by factors such as precipitation levels, temperature, and soil quality |
Types of Grasslands
Grasslands can be divided into several different types based on their geographic location and the dominant plant species. Some common types of grasslands include:
Tropical Grasslands
Tropical grasslands, also known as savannas, are found near the equator and are characterized by high temperatures and seasonal patterns of rainfall. They are home to a wide variety of grass and herb species, as well as scattered trees and shrubs. Some examples of tropical grassland plants include elephant grass, acacia trees, and baobab trees. These grasslands tend to have a greater diversity of grasses and herbs, and support a high diversity of fauna, like elephants, lions, zebras, among others.
Temperate Grasslands
Temperate grasslands are found in regions with moderate temperatures and moderate to low levels of precipitation. They are characterized by the presence of grasses and herbs, such as buffalo grass, blue grama and wildflowers. Some examples of temperate grassland include the Great Plains of North America and the steppes of Asia. These grasslands are characterized by less rainfall and a dominance of grasses over herbs.
Montane Grasslands
Montane grasslands, also known as alpine meadows or tundra, are found at high altitudes in mountainous regions and are characterized by low temperatures and short growing seasons. They are typically composed of hardy grasses, sedges, and low-lying shrubs. Some examples of montane grassland plants include bluegrass, sagebrush, and alpine forget-me-not. These grasslands are important habitats for wildlife that are adapted to high altitude, such as mountain goats and bighorn sheep.
| Type of Grassland | Characteristics | Examples of Plants |
|---|---|---|
| Tropical Grasslands | high temperatures, seasonal rainfall, grasses, herbs, scattered trees and shrubs | Elephant grass, Acacia trees, Baobab trees |
| Temperate Grasslands | moderate temperatures, moderate to low precipitation, grasses, herbs | Buffalo grass, Blue grama, Wildflowers |
| Montane Grasslands | high altitudes, low temperatures, short growing seasons, hardy grasses, sedges, low-lying shrubs | Bluegrass, Sagebrush, Alpine forget-me-not |
Ecological Importance of Grasslands
Grasslands play an important role in maintaining the balance of the planet’s climate and weather patterns, and are also vital for the survival of many plant and animal species.
Grasslands serve as habitats for many species of grazing animals, such as bison, buffalo, and antelope, which play an important role in shaping the grassland ecosystem. Their grazing habits can help control the growth of invasive plant species, and their manure helps to fertilize the soil.
Grasslands also play a key role in carbon sequestration, they store large amounts of carbon in their soil, and they are also able to remove large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This not only helps to mitigate the effects of climate change, but also helps to improve air and water quality.
Grasslands are also important for biodiversity. They are home to a wide variety of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else on earth. These habitats support many species of birds, insects, reptiles, and small mammals, including many threatened and endangered species.
Grasslands also provide important ecosystem services such as soil conservation, water regulation, and pollination. Their deep roots systems help to prevent soil erosion and improve soil health, and their ability to absorb and release large amounts of water helps to regulate the water cycle. They also provide important habitats for pollinators such as bees and butterflies, which are essential for the health of many plant and animal species.
| Ecological Importance | Description |
|---|---|
| Climate and Weather regulation | Grasslands play an important role in regulating the water cycle, by absorbing and releasing large quantities of water, which in turn can help to mitigate the effects of drought and flooding. They also play a key role in carbon sequestration, they store large amounts of carbon in their soil, and they are also able to remove large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, which improves air and water quality. |
| Biodiversity | Grasslands are home to a wide variety of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else on earth, including many threatened and endangered species, they also support many species of birds, insects, reptiles, and small mammals. |
| Ecosystem services | Grasslands provide important ecosystem services such as soil conservation, water regulation, and pollination, their deep roots systems help to prevent soil erosion and improve soil health, they provide important habitats for pollinators such as bees and butterflies, which are essential for the health of many plant and animal species. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, Grasslands are habitats of great ecological importance, they support a wide variety of plant and animal species and play an important role in maintaining the balance of the planet’s climate and weather patterns. Understanding the characteristics and types of Grasslands, as well as their ecological importance, can help us to better understand and appreciate the diversity of plant life on our planet, and take steps to protect and preserve these vital habitats.