Mountain Habitat
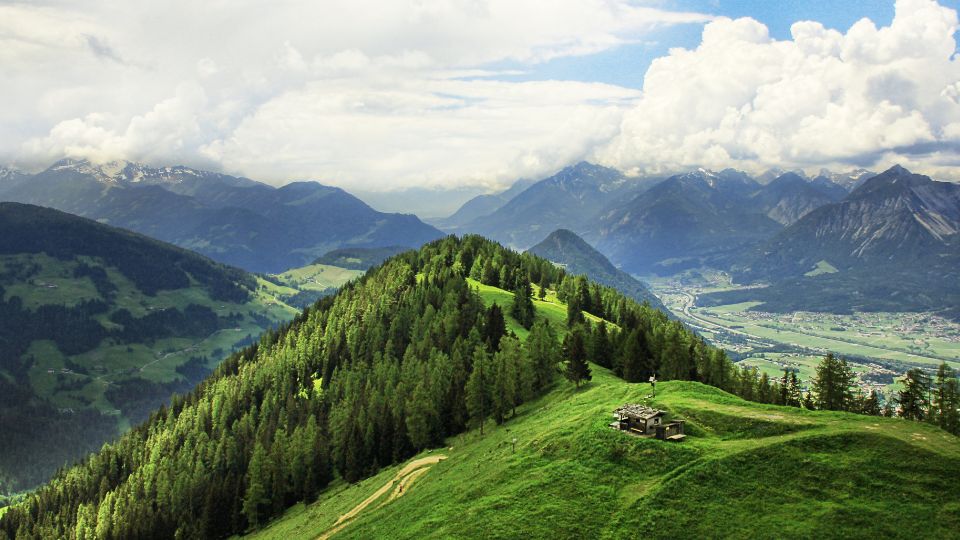

Mountains are one of the most varied and complex habitats on Earth, and they support a wide variety of plant species that have adapted to the unique conditions of high altitude. In this article, we will take a closer look at the characteristics of mountain habitats, the different types of mountain habitats, and their ecological importance.
Characteristics of Mountain Habitats
Mountains are characterized by their high elevations and harsh environments, which create unique conditions that shape the adaptations of the plants that call them home. Some key characteristics of mountain habitats include:
Elevation
The main characteristic of mountain habitats is the elevation. As you go up in elevation the temperature decreases and the atmosphere gets thinner making the oxygen content less. This affects the way the plants grow and adapt to their environment.
Slope and Aspect
Another important characteristic is the slope and aspect of the mountain. This can affect the amount of sunlight and wind that reaches a particular area and also can affect the temperature and moisture levels.
Soil
Mountain habitats also have unique soil conditions, often characterized by rocky, nutrient-poor soils that are high in minerals. This can affect the types of plants that are able to grow in a particular area.
Climate
The climate of mountain habitats can vary widely depending on the location and elevation. At high elevations, temperatures can be much colder and precipitation can be greater than at lower elevations. This can affect the types of plants that are able to survive in a particular area.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Elevation | The main characteristic of mountain habitats is the elevation. As you go up in elevation the temperature decreases and the atmosphere gets thinner making the oxygen content less. |
| Slope and Aspect | The slope and aspect of the mountain can affect the amount of sunlight and wind that reaches a particular area and also can affect the temperature and moisture levels. |
| Soil | Mountain habitats have unique soil conditions, often characterized by rocky, nutrient-poor soils that are high in minerals. |
| Climate | The climate of mountain habitats can vary widely depending on the location and elevation. At high elevations, temperatures can be much colder and precipitation can be greater. |
Types of Mountain Habitats
Mountains can be divided into several different types based on their geographic location, the type of soil, and the dominant plant species. Some common types of mountain habitats include:
Alpine Tundra
Alpine Tundra is a high-elevation habitat above the tree line, characterized by short-stature plants, such as mosses, lichens, and low-growing shrubs. This habitat is often found in high-altitude areas such as the Rocky Mountains, the Andes, and the Himalayas.
Subalpine Forest
Subalpine Forest is a habitat found at lower elevations below the alpine tundra, characterized by coniferous trees such as spruces, firs, and pines. This habitat is often found in areas with high precipitation and moderate temperatures.
Montane Forest
Montane Forest is a habitat found at lower elevations than the subalpine forest, characterized by a wide variety of tree species that are adapted to the specific conditions of high altitude, such as lower temperatures and lower levels of oxygen.
| Type of Mountain Habitat | Characteristics | Examples of Plants |
|---|---|---|
| Alpine Tundra | High-elevation habitat above the tree line, characterized by short-stature plants, such as mosses, lichens, and low-growing shrubs | Mosses, Lichens, Alpine flowers |
| Subalpine Forest | Lower elevations below the alpine tundra, characterized by coniferous trees such as spruces, firs, and pines. | Spruces, Firs, Pines |
| Montane Forest | Lower elevations than the subalpine forest, characterized by a wide variety of tree species that are adapted to specific conditions of high altitude | Oak, Beech, Maple |
Ecological Importance of Mountains
Mountains play an important role in the Earth’s ecosystems. They are often called “water towers” as they are the source of many rivers, streams, and lakes and provide water to millions of people and animals. They also provide important habitats for a wide variety of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else on earth.
Mountains also play a key role in climate regulation, acting as a barrier that influences the formation of different climate zones and weather patterns. For example, mountain ranges like the Himalayas and the Andes act as rain shadows, creating dry, arid regions on the leeward side of the mountains, while the windward side receives higher levels of precipitation.
They also play a key role in carbon sequestration, they store large amounts of carbon in their soil, and they are also able to remove large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through the process of photosynthesis.
Mountain habitats are also important for recreation and tourism, providing opportunities for activities such as hiking, climbing, skiing and snowboarding. Many mountain ranges are also home to ancient cultural and spiritual traditions, making them sacred sites for many people around the world.
Despite the many ecological and cultural values of mountain habitats, they are under threat from human activities such as mining, logging, and urbanization. Climate change is also having a severe impact on mountain habitats, with rising temperatures and changes in precipitation patterns, threatening the survival of the plant and animal species that call these habitats home. It is important that efforts are made to conserve and protect mountain habitats for the survival of the plant and animal species, as well as for the services they provide for the entire planet.
| Ecological Importance | Description |
|---|---|
| Climate regulation | Mountains act as a barrier that influences the formation of different climate zones and weather patterns, influencing precipitation, temperature and other meteorological factors. |
| Carbon sequestration | They store large amounts of carbon in their soil, and are also able to remove large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through the process of photosynthesis. |
| Biodiversity | They provide important habitats for a wide variety of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else on earth. |
| Water source | They are often called “water towers” as they are the source of many rivers, streams, and lakes and provide water to millions of people and animals. |
| Recreational and Tourism | They provide opportunities for activities such as hiking, climbing, skiing and snowboarding, many mountain ranges are also home to ancient cultural and spiritual traditions, making them sacred sites for many people around the world. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, mountain habitats are one of the most varied and complex habitats on earth, they support a wide variety of plant species, and provide many vital ecosystem services. Understanding the characteristics and types of mountain habitats, as well as their ecological importance, can help us to better understand and appreciate the diversity of plant life on our planet, and take steps to protect and preserve these vital habitats. By conserving and protecting mountain habitats, we can ensure that these habitats continue to provide the many benefits that they offer for generations to come.