Thallophyta

Thallophyta, also known as thallogens, thallophytes, is a division of non-vascular plants that includes a diverse group of organisms such as algae, fungi, and lichens. These organisms are characterized by having a thallus, or undifferentiated body, instead of distinct leaves, stems, and roots. They are considered as the simplest forms of plant life and play a vital role in the ecosystem. They are found in a wide range of environments, from freshwater to terrestrial, and can be unicellular or multicellular. In this article, we will explore the characteristics, classification, and importance of Thallophyta, including their reproduction, growth, and ecological significance.
What is Thallophyta?
Thallophyta is a division of non-vascular plants, which includes algae, fungi, and lichens. They are characterized by having a thallus, or undifferentiated body, instead of distinct leaves, stems, and roots. They reproduce through spores and lack true roots, stems and leaves. They are considered as the simplest forms of plant life.
Characteristics of Thallophyta
- They do not have true roots, stems, or leaves
- They reproduce asexually or sexually
- They have a simple body structure, often consisting of a single cell or a filamentous or leaf-like structure
- They can be found in a variety of environments, including freshwater, marine, and terrestrial
- They can be autotrophic (able to produce their own food) or heterotrophic (dependent on other organisms for food)
- They play a critical role in the ecosystem, acting as primary producers and decomposers
- Some species have medicinal and economic importance.
Classification of Thallophyta
Thallophyta is a broad and diverse group of non-vascular plants that includes a wide range of organisms, such as algae, fungi, and lichens. They are classified into several groups based on their characteristics and characteristics.
- Algae: Algae are photosynthetic organisms that can be found in a variety of environments, including freshwater, marine, and terrestrial. They are classified into several groups, such as green algae, brown algae, red algae, and blue-green algae.
- Fungi: Fungi are heterotrophic organisms that are classified into several groups, such as yeasts, molds, and mushrooms. They play a critical role in the ecosystem as decomposers and symbionts.
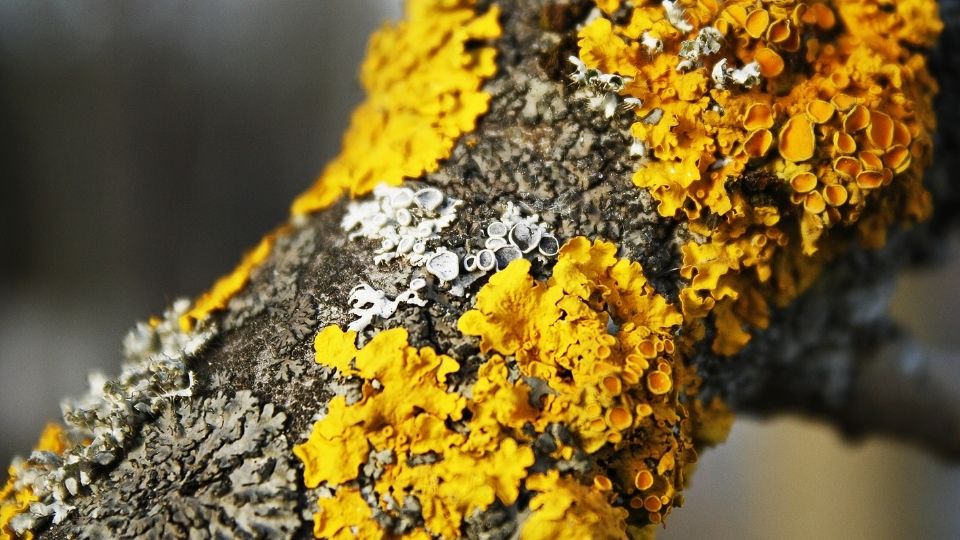
- Lichens: Lichens are symbiotic organisms that consist of a fungus and an alga or a cyanobacterium. They can be found in a variety of environments and are classified into several groups, such as crustose, foliose, and fruticose lichens.
In summary, Thallophyta can be classified into three main groups: Algae, Fungi and Lichens, each one of them can be further subdivided into different groups, depending on their characteristics and characteristics, such as the type of reproduction, pigmentation, shape, and ecological role.
Importance of Thallophyta
Thallophyta, also known as thallophytes or thallogens, are a diverse group of non-vascular plants that include algae, fungi, and lichens. They play a critical role in the ecosystem and have many important uses for humans.
| Group of Thallophyta | Importance |
|---|---|
| Algae | 1. Primary producers in aquatic ecosystems, providing food for aquatic animals and helping to maintain the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the water. 2. Used as food and medicine by humans, as well as in industrial applications such as the production of biofuels and cosmetics. 3. Some species used in biotechnology and bioremediation. |
| Fungi | 1. Decomposers in terrestrial ecosystems, breaking down dead plant and animal matter and recycling nutrients. 2. Some species have medicinal uses, such as the production of antibiotics and immunosuppressants. 3. Some species are used in the production of food and beverages, such as bread, cheese, and beer. 4. Some species of fungi play important role in plant growth and health by forming mycorrhizal associations with plant roots. |
| Lichens | 1. Indicator of air quality and environmental health, as they are sensitive to pollutants. 2. Used as food by some animals and as traditional medicine by some indigenous cultures. 3. Some species used in biomonitoring and bioremediation. 4. They play an important role in the ecosystem as colonizers of bare rocks and soils, helping to break down and weather the substrate, preparing it for other organisms to colonize. |
In summary, Thallophyta play a critical role in the ecosystem as primary producers, decomposers, and symbionts, and they have many important uses for humans, including as food, medicine, and in industrial and environmental applications.
Examples of Thallophyta
Here are several examples of thallophytes:
- Algae: Chlamydomonas (a green algae), Kelp (a brown algae), Porphyra (a red algae), Nostoc (a blue-green algae)
- Fungi: Agaricus bisporus (white button mushroom), Penicillium (a mold), Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast)
- Lichens: Cladonia (a fruticose lichen), Parmelia (a foliose lichen), Rhizocarpon geographicum (a crustose lichen)
An example of a thallophyte is the green alga Spirogyra. It is a freshwater alga that forms green filaments in ponds, ditches, and slow-moving streams. Spirogyra is a simple organism, with a filamentous body structure composed of elongated cells arranged end-to-end. Each cell contains chlorophyll, which allows it to carry out photosynthesis. Spirogyra reproduces both sexually and asexually, with sexual reproduction involving the fusion of two different filaments.
Another example of thallophyte is the fungus Agaricus bisporus, commonly known as the white button mushroom. It is a type of edible mushroom that is widely cultivated for its taste and nutritional properties. Agaricus bisporus is a heterotrophic organism, which means it obtains its food from other organisms. It has a gilled fruiting body, a stalk and a cap, which plays a role in reproduction. The gills on the underside of the cap produce spores that can be dispersed by wind to start new colonies.
Lichens are another example of thallophytes, an example of which is the crustose lichen Rhizocarpon geographicum which can be found growing on rocks, soils and tree trunks in cold and temperate regions. This lichen is composed of a fungus and a green alga or cyanobacterium that live in symbiosis. The alga or cyanobacterium uses photosynthesis to produce food, while the fungus provides a structural support and protection.
Thallophyta Plants
Here is a list of thallophyte plants:
- Algae: Spirogyra, Chara, Cladophora, Oedogonium, Ectocarpus, Porphyridium
- Fungi: Agaricus bisporus, Pleurotus ostreatus, Ganoderma lucidum (Reishi mushroom), Coprinus comatus (Shaggy Mane Mushroom), Auricularia auricula (Jelly Ear Mushroom)
- Lichens: Cladonia, Parmelia, Rhizocarpon geographicum, Evernia prunastri (Oak moss lichen), Usnea barbata (Bearded lichen)
Conclusion
In conclusion, Thallophyta is a diverse group of non-vascular plants that includes algae, fungi, and lichens. They play a critical role in the ecosystem as primary producers, decomposers, and symbionts, and they have many important uses for humans, including as food, medicine, and in industrial and environmental applications. They can be found in various environments, including freshwater, marine, and terrestrial and have different characteristics that allow them to survive and adapt to the different conditions. Algae, Fungi, and Lichens are the main sub-divisions of thallophytes and each of them can be further subdivided into different groups based on their characteristics and characteristics, such as the type of reproduction, pigmentation, shape, and ecological role.