Wetland Habitat
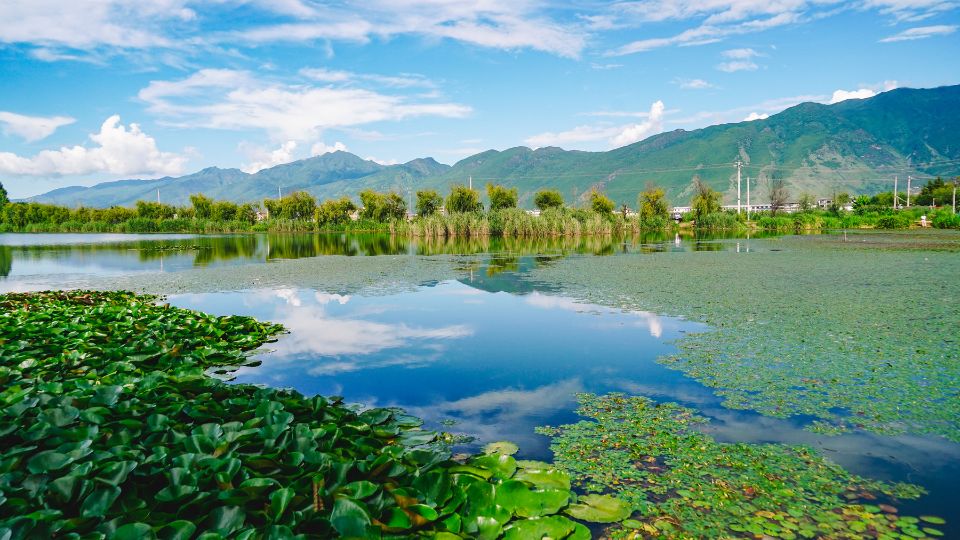

Wetlands are areas of land that are saturated with water, either permanently or seasonally. These habitats are characterized by a unique combination of water and land, and they support a wide variety of plant species that have adapted to these conditions. In this article, we will take a closer look at the characteristics of wetlands as a habitat for plants, the different types of wetlands, and their ecological importance.
Characteristics of Wetland Habitats
Wetlands are defined by their water-saturated soils and the presence of hydrophytic plants, which are plants adapted to living in wet conditions. Some key characteristics of wetlands include:
Water saturation
Wetlands are saturated with water either permanently or seasonally. This saturation creates an environment with unique soil conditions and hydrology, which shape the adaptations of the plants that call wetlands home.
Hydrophytic plants
Wetlands are home to a variety of hydrophytic plants, which are plants adapted to living in wet conditions. These plants have a range of adaptations to survive in these conditions, such as buoyant stems and leaves or the ability to tolerate waterlogged soils.
High biodiversity
Wetlands are known for their high biodiversity, they support a wide variety of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else on earth. Wetlands also provide important ecosystem services such as water purification, flood control, and carbon sequestration.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Water saturation | Wetlands are saturated with water either permanently or seasonally. This saturation creates an environment with unique soil conditions and hydrology. |
| Hydrophytic plants | Wetlands are home to a variety of hydrophytic plants, which are plants adapted to living in wet conditions. They have a range of adaptations such as buoyant stems and leaves or the ability to tolerate waterlogged soils. |
| High biodiversity | Wetlands are known for their high biodiversity, they support a wide variety of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else on earth. |
| Water purification | Wetlands act as natural filters, removing pollutants and excess nutrients from the water that flows through them. |
| Habitat | Wetlands provide important habitat for a wide variety of plant and animal species, including waterfowl, fish, migratory birds, mammals, reptiles, amphibians, and insects. |
Types of Wetlands
Wetlands can be divided into several different types based on their geographic location, the type of water present, and the dominant plant species. Some common types of wetlands include:
Marshes
Marshes are wetlands that are dominated by herbaceous plants, such as cattails, reeds, and rushes. They are found in a variety of environments, including freshwater, saltwater, and tidal areas.
Swamps
Swamps are wetlands that are dominated by woody plants, such as trees and shrubs. They are found in a variety of environments, including freshwater and saltwater areas.
Bogs
Bogs are wetlands that are characterized by acidic water, spongy peat soils, and a dominance of mosses and other acid-loving plants. They are found in areas with high precipitation, such as high altitudes or the northern latitudes.
Fens
Fens are wetlands that are characterized by neutral or alkaline water and a dominance of grasses and sedges. They are found in areas with moderate precipitation and are often fed by groundwater or surface water that is rich in minerals.
| Type of Wetland | Characteristics | Examples of Plants |
|---|---|---|
| Marshes | Saturated with water and dominated by herbaceous plants such as cattails, reeds, and rushes, found in freshwater, saltwater, and tidal areas | Cattails, Bulrushes, Sea lavender |
| Swamps | Saturated with water and dominated by woody plants such as trees and shrubs, found in freshwater and saltwater areas | Cypress, Mangrove, Black willow |
| Bogs | characterized by acidic water, spongy peat soils, and a dominance of mosses and other acid-loving plants, found in areas with high precipitation | Sphagnum moss, Labrador tea, Blueberries |
| Fens | characterized by neutral or alkaline water and a dominance of grasses and sedges, found in areas with moderate precipitation | Sweetflag, Cattails, Sedges |
Ecological Importance of Wetlands
Wetlands are one of the most productive habitats on earth, and they support a wide variety of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else on earth. They also provide a wide range of ecological services that are essential for the health of our planet.
One of the most important roles of wetlands is water purification. Wetlands act as natural filters, removing pollutants and excess nutrients from the water that flows through them. This helps to improve the overall water quality in rivers, streams, and other bodies of water.
Wetlands also provide important habitat for a wide variety of plant and animal species. They provide breeding and nesting grounds for waterfowl, fish, and other aquatic species, and they are also important stopover sites for migratory birds. Wetlands also support many species of mammals, reptiles, amphibians, and insects, many of which are threatened or endangered.
In addition to their ecological importance, wetlands also have significant economic value. They provide important resources such as fish, timber, and other plant materials that are used in a wide variety of industries. Wetlands also provide important recreational opportunities, such as hunting, fishing, and wildlife watching.
Despite the benefits they provide, wetlands are one of the most threatened habitats on earth. They are being lost at an alarming rate due to human activities such as urbanization, agriculture, and resource extraction. It is important that efforts are made to conserve and protect these habitats for the survival of the plant and animal species that call wetlands home, as well as for the services they provide for the entire planet.
| Ecological Importance | Description |
|---|---|
| Water purification | Wetlands act as natural filters, removing pollutants and excess nutrients from the water that flows through them, improving water quality in rivers, streams, and other bodies of water. |
| Habitat | Wetlands provide important habitat for a wide variety of plant and animal species, including waterfowl, fish, migratory birds, mammals, reptiles, amphibians, and insects many of which are threatened or endangered. |
| Ecosystem services | Wetlands provide important ecosystem services such as water purification, flood control, carbon sequestration, recreation and tourism, fish and wildlife production and protection of coastal areas |
| Economic Value | Wetlands provide important resources such as fish, timber, and other plant materials used in various industries. They also provide important recreational opportunities, such as hunting, fishing, and wildlife watching. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, wetlands are habitats of great ecological importance, they support a wide variety of plant and animal species, and provide many vital ecosystem services. Understanding the characteristics and types of wetlands, as well as their ecological importance, can help us to better understand and appreciate the diversity of plant life on our planet, and take steps to protect and preserve these vital habitats. By conserving and protecting wetlands, we can ensure that these habitats continue to provide the many benefits that they offer for generations to come.